Cyber Attacks and Intrusion Detection
Cyberthreats are now one of the most urgent concerns in the world as in last decade, the world has witnessed a staggering growth in digital inclusion, this massive gathering around the internet has also given new proportions to a long standing challenge in technology Cyber Attacks
A cyberattack is a malicious and deliberate attempt by an individual or organization to breach the information system of another individual or organization, Wrong handling of client data in any function of the web application introduces a security weakness which can probably be exploited by an attacker. To name a few, attack types like buffer overflows, SQL or code injections, Cross-Site Scripting emerge from few common pitfalls. Accordingly, for businesses and organizations, detecting and preventing cyber-attacks are of significant importance today. Another approach in protecting web-based applications, besides writing robust code, is the domain of intrusion detection systems (IDS) to enable prevention mechanisms or early warning.
IDS techniques can be distinguished into misuse detection and anomaly detection based on the style of detection. While misuse detection relies on proper signatures of malicious behavior, anomaly detection tends to use methods such as machine learning or statistics to construct a profile of normal behavior and report deviating interactions as anomalies.
Intrusion detection systems are used to detect anomalies with the aim of catching hackers before they do real damage to a network. They can be either network- or host-based. A host-based intrusion detection system is installed on the client computer, while a network-based intrusion detection system resides on the network.
Accuracy of IDS: Confusion Matrix
The detection performance of misuse detection completely depends on currentness and coverage of signatures, but false-alarm rates are accordingly low. Anomaly detection is prone to costly false-alarm rates, but it is more probable by design to recognize novel attacks.
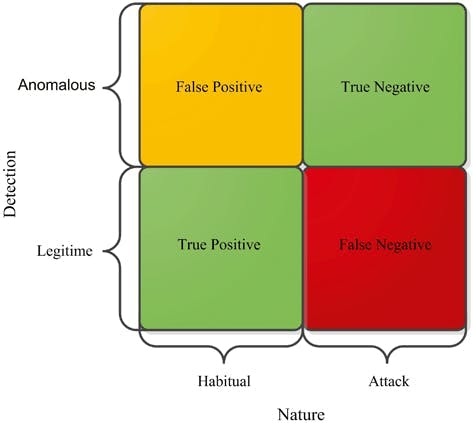
A confusion matrix is a tubular summary of number of activities that are identified as correct and incorrect by IDS, in terms of the accuracy of an IDS, there are four possible states for each activity:
True positive state is when the IDS identifies an activity as an attack and the activity is actually an attack that is successful identified as an attack.
True negative state is similar. This is when the IDS deems an activity as acceptable behavior and the activity is actually acceptable. A true negative is successfully ignoring acceptable behavior.
As the IDS is performing as expected, thus neither of these states is harmful.
False-positive is the term used to indicate a file or item that is marked as malicious, but, in fact, it isn’t.
False-negative is the opposite. It is a case when a malicious file or item is labeled as secure, clean.
False-positive and false-negative are errors and failures found in protection solutions that fail to label files and items correctly. Now we'll know how these errors are harmful to the system.
False-negative:
A false negative state is the most serious and dangerous state. That is, a false negative is when the IDS fails to catch an attack. These advanced/hidden cyber threats are capable of evading prevention technologies that are trained to look for “known” attacks and malware because No cybersecurity or data breach prevention technology can block 100% of the threats they encounter. The main reason for false-negative occurrence refers to a new threat or, as we say, a zero-day attack.
False-positive:
False positives are mislabeled security alerts, indicating there is a threat when in actuality, there isn’t. These false/non-malicious alerts (SIEM events) increase noise for already over-worked security teams and can include software bugs, poorly written software, or unrecognized network traffic.
By default, most security teams are conditioned to ignore false positives. Unfortunately, this practice of ignoring security alerts — no matter how trivial they may seem — can create alert fatigue and cause your team to miss actual, important alerts related to a real/malicious cyber threats.
How to prevent false positive and false negative?
- Research Artificial Intelligence Solutions:
Tackle the problems associated with false positives and negatives through the power of modern AI advancements. Its context-aware AI monitors your network to gain a baseline understanding of your systems and how they have been used. Equipping your network security team with a tool that will help them better analyze emerging trends and widespread security threats will leave your company less vulnerable to actual security breaches.
- In the fight against false positives and false negatives, the first step is to realize that ignoring certain security alerts isn’t the answer and that better security technology is needed to automate accurate threat detection